SSH, or Secure Shell, is an encrypted protocol and associated program intended to replace telnet. It can also be used for creating secure tunnels, somewhat akin to Virtual Private Networks, and for use as a network file system. Unless changed, everything SSH operates on port 22. What Are SSH Clients for Windows, Mac, and Unix. PuTTY is a free open-source terminal emulator which lets you initiate interactive command-line sessions to UITS Unix servers. It can act as a client for the SSH, Telnet, rlogin, and raw TCP computing protocols and as a serial console client.
Telnet and SSH are the general purpose client server application program and uses remote terminal service which allows a user at one site to interact with a remote time-sharing system at another site as if the user's keyboard and a display connected directly to the remote machine.
The main difference between Telnet and SSH is that the Telnet is conventional protocol whereas SSH is the replacement for Telnet protocol and also SSH have enhanced features.
Content: Telnet Vs SSH
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | Telnet | SSH |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Less secured | Highly secured |
| Uses port number | 23 | 22 |
| Data format | Telnet transfers the data in plain text. | Encrypted format is used to send data and also uses a secure channel. |
| Authentication | No privileges are provided for users authentication. | Uses public key encryption for authentication. |
| Suitability of network | Private networks are recommended. | Suitable for Public networks. |
| Vulnerabilities | Vulnerable to security attacks. | SSH has overcome many security issues of telnet. |
| Bandwidth Usage | Low | High |
Definition of Telnet
TELNET is a client-server program that permits the user to retrieve any application program on a remote computer. The function of a telnet is to provide the services to the user on the remote computer and transferring the result to the local computer. TELNET is an acronym for TErminal NETwork. TELNET facilitates the establishment of the connection to a remote system in a manner that the local terminal resembles to be a terminal at the remote system.
Remote Login
Whenever a user intends to access an application program or utility placed on a remote machine, then user performs Remote Login. Here the TELNET client server program is utilized. The user enters the keystrokes to the terminal driver, which is then accepted as characters by the local operating system.
However, characters are not interpreted. The characters are transmitted to TELNET client and converted into a universal character group refer to as Network Virtual Terminal characters. Then these characters are delivered to the local TCP/IP stack.
The text and commands in NVT format move through the internet and reaches the TCP/IP stack at the remote machine. After transferring the characters to the operating system, it is then passed to the TELNET server, which alters the characters to the corresponding intelligible characters translated by the remote computer.
The characters are moved to the terminal driver as it is not intended to accept characters from a TELNET server. The solution is to add a piece of software known as a pseudo terminal driver which behaves as the characters are transmitted from the terminal. At last, the operating system moves the characters to the appropriate application program.
Although TELNET is widely used and is not as complex as some remote terminal protocols. Usually, TELNET client software permits the user to describe a remote machine either by the giving its domain name or IP address.
The three type of basic services that TELNET offers are:
- It determines a virtual network terminal that renders a standard interface to remote systems.
- It provides a set of standard options and includes a mechanism that permits the client and server to transact options.
- It allows an arbitrary program to become a client or either end can negotiate options.
Definition of SSH
SSH (Secure SHell) is a network protocol which provides a substitution for vulnerable remote login and command execution provision, such as telnet, rlogin and rsh. It encrypts traffic in both directions, preventing traffic, sniffing and password theft. SSH also gives multiple supplementary features like compression, public key authentication, Authentication of the server, port forwarding, X11 forwarding, file transfer.
SSH also provides remote command execution. When you log in, a pseudo-terminal is assigned to your session and your session, will remain open until you explicitly log out or is terminated from the server end. This protocol supports functionalities like Secure command-shell, secure file transfer and port forwarding.
- Secure Command Shell: It allows a user to view the contents of directories, edit files and access custom database applications remotely.
- Secure file transfer: It acts as a subsystem of the secure shell protocol. Essentially, Secure file transfer protocol is a separate protocol layered over the SSH protocol to handle the transfer of a file.
- Port forwarding: It is also known as tunnelling, which provides the basic security for the TCP/IP application.
Key Differences Between Telnet and SSH
- Telnet and SSH both serve the same purpose and provides the connectivity to the remote server but Telnet is conventional protocol, although it is still in use in the various application. SSH is the replacement for Telnet and has some enhanced features too.
- Telnet doesn't provide any security mechanism whereas SSH is more secure and provides security measures.
- In Telnet transmits data in plain text that is the reason it is vulnerable to security attacks. On the other hand, SSH uses encryption for transmitted data and security breach does not likely occur. SSH can withstand eavesdropping, man in the middle and insertion/ replay attacks.
- Telnet doesn't provide authentication facility while SSH provides user authentication.
- Telnet works with a private network. In contrast, SSH works with a public network.
- Telnet communicates via port number 23 over TCP/IP. As against, SSH uses port number 22 for communication.
Conclusion
The SSH protocol is a somewhat better replacement for Telnet as SSH has security measures. While Telnet does not provide much security although still in use.
Related Differences:
From DD-WRT Wiki
English • Deutsch • Español • Français • Italiano • 日本語 • Polski • Português • Русский • Svenska • 中文(中国大陆) • 中文(台灣) • |
You are here: DD-WRT wiki mainpage / Scripting / SSH/Telnet & The CLI
|
[edit] Using Telnet
- Open the command prompt and type 'telnet' (On Windows vista/7 you will need to install it from 'programs and features').
- connect to e.g. 192.168.1.1 so in the command prompt, this would look like:
- When asked for the username, enter root (even if you changed username in web interface)
- When asked for the password, enter your router's password (default 'admin')
[edit]Overview
SSH, or Secure Shell, is an encrypted protocol and associated program intended to replace telnet. It can also be used for creating secure tunnels, somewhat akin to Virtual Private Networks, and for use as a network file system (Sshfs). Unless changed, everything SSH operates on port 22.
SSH operates just as telnet with a user/password combination or on a Public/Private key infastructure. For the latter to work, a small public key is given to the server and the server gives your client its public key. Your client encrypts information to the server using the servers public key and the server encrypts information sent to you using your public key. Private keys are never exchanged, and are used to decrypt the information encrypted with the associated public key.
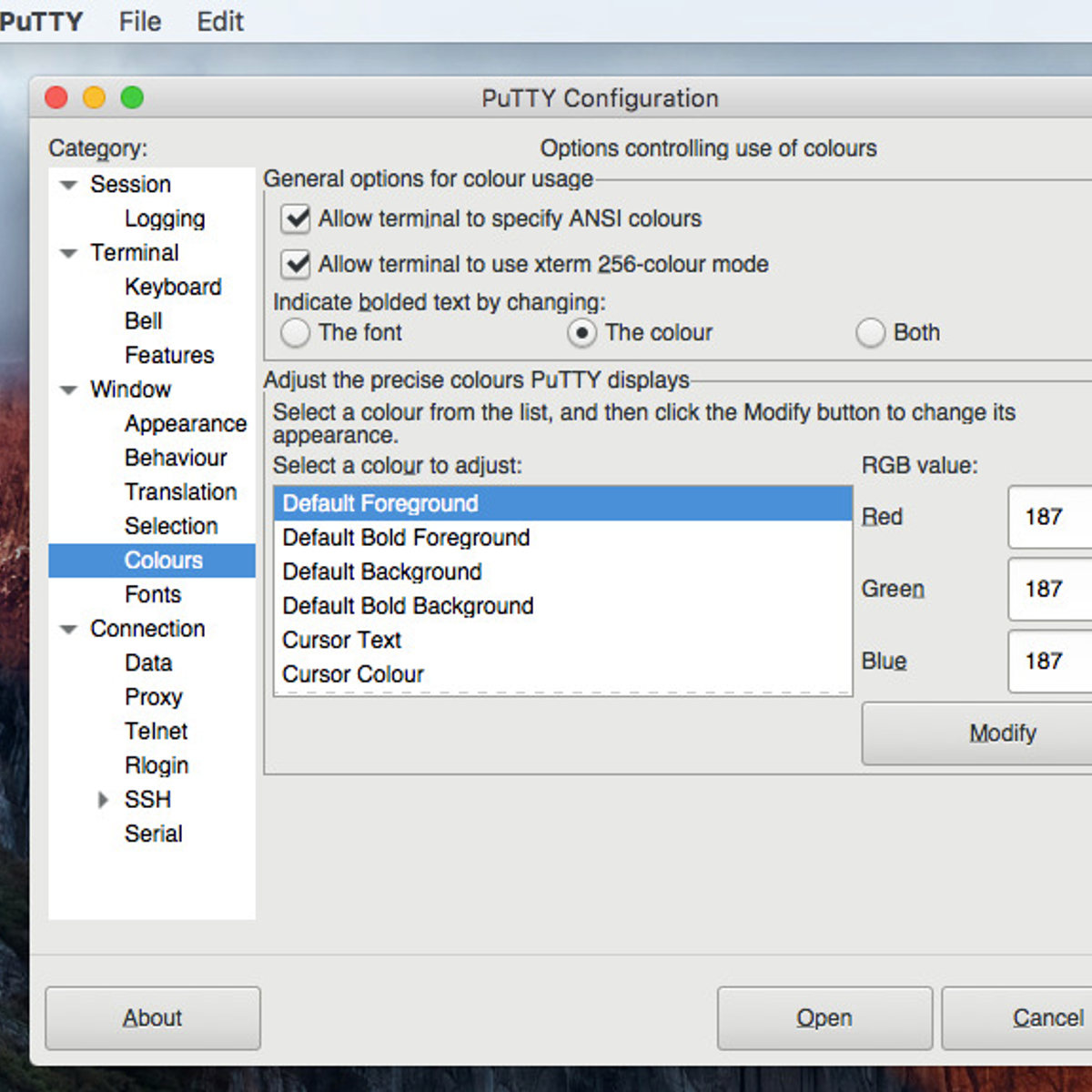
The DD-WRT firmware can use user/pass logon or only allows connections from clients whose public keys are manually entered via the web interface. Multiple keys can be entered by placing them on separate lines.
If you want to use user/password to login using SSH use user 'root' with the password you set in the webinterface
Actually you can manually set (via telnet or ssh) the sshd_authorized_keys nvram variable.ie nvram set sshd_authorized_keys=key1 key2 key3 etc
You can also manually edit /tmp/root/.ssh/authorized_keys and add keys (although these will disappear on a reboot unless you have a startup script altering them).
It is worth pointing out ssh keys are quite long strings of characters so if you paste them in youhave to be careful that you don't get any line breaks (ie it is one Long continuous line).or they will not work.
[edit]Setting Up
[edit]Public key method
Public key authentication is one of the most secure methods of logging into SSH. It functions similar to HTTPS, as all transmissions are encrypted with a key that only the client and server will have. Another plus..if you use this method instead of password authentication, no one will be able to crack away at your router trying to guess the password!
To enable it, first you should generate a Public/Private key pair on your desktop machine. This can be done through the 'Puttygen' utility if you're using either Putty or WinSCP as clients. Copy the public key to the clipboard and save the private key somewhere on your computer. There is no need to save the public key. If you forget it, you can instruct Puttygen to open your private key file rather than generating a new key pair and it will tell you your public key. Users of non-windows environments may use the ssh-keygen(1) utility:
Download iMovie 10.1.14 for Mac OS. IMovie is an integrated Apple-based application that serves users as an efficient, highly-effective and intuitive multimedia editing application. Create a new iMovie project. Learn how to set up a new project and add content to it on your. Just click to download and install on your Mac or iOS device. Download iMovie for iOS Download iMovie for macOS. Clips is a free iOS app for making and sharing fun videos with text, effects, graphics and more. Download imovie for mac. Download and Install iMovie. Download for PC - server 1 - MAC: Download for MacOS - server 1 - Free Thank you for visiting our site. Have a nice day! From the first scene to the last. Whether you're using a Mac or an iOS device.
It is recommended that you don't secure your key pair with a password, as this will make things easier for you, although somewhat less secure.
- Using the Web Interface, go to the Administration tab. (in v24 use Services tab)
- Under the Services sub-tab, Enable SSHd in the Secure Shell section. If new options don't appear, Save Settings
- Paste your public key in the authorized key of the SSHD section that has now expanded. You will need to generate this on your desktop if you don't have one yet.
- Save and Apply Settings
NOTE: The format of the public key when pasted has to be 'ssh-rsa', space, key, space, comment. Here is an example: (please note that there should be no line feed at the end)
Alternate method:
Remember to enter your key as an entire characters line (no space, tab..)
In Putty, you can enable key authentication by opening the SSH authentication configuration (Connection -> SSH -> Auth) and entering or browsing to your private key file. Also make sure your auto-login username is root (in Connection -> Data).
[edit]Password Login method
If you don't want the hassle of generating ssh keys, you may use the password logon method. However, please be aware that this method is much less secure! (passwords may be truncated to 8 characters or less)
- Using the Web Interface, go to the Administration tab. (in v24 use Services tab)
- Under the Services sub-tab, Enable SSHd in the Secure Shell section. If new options don't appear, Save Settings
- Enable Password Login to enable the password login
- Save and Apply Settings
After this you may login as user 'root' with the password you set for the webinterface
Install Telnet Mac
[edit]Automatic Login (for shell scripts)
The Dropbear SSH client allows you to specify the password through an environment variable. This is useful when you need dd-wrt to auto-login to another host via SSH.
[edit]Security Tips
- Choose a random, non-standard port number >1024, especially if you enabled SSH access from the Internet! Most attackers will use a port scanner that only scans for common open ports by default. Scanning all 65535 ports is much slower for them, which makes it more difficult to find an attack vector and also more likely to be flagged by an Intrusion Detection System.
- Memorize, or record somewhere safe, your router's key fingerprint! In the process of logging into your router, if you see that the key fingerprint matches, you can rest assure noone is spying on your connection (i.e. via man-in-the-middle attack). If the key fingerprint does NOT match (your SSH client would likely notify you of this), something is wrong and you should consider terminating the connection immediately! (Note: the router's key fingerprint may change upon reset and/or upgrade, as it will likely generate a new key pair)
- For even more added security when using the public key method, you can password protect your private key. This way, if someone malicious happens to get ahold of it, they will still not be able to log into your router without first cracking the password of the key. Otherwise, if the keys are unprotected, anyone who stumbles upon them could likely gain immediate root access to your router and network.
[edit]SSH Shell Client
Provides a secure alternative to standard telnet.
A good Windows Client to use is Putty
Configure the client to use the Private Key you saved earlier.
Most Linux distros have telnet and SSH clients by default.
[edit]SSH Port Forwarding
SSH port forwarding is the ability to create encrypted tunnels to pass traffic through, sort of like a VPN. Below we will discuss two different approaches to SSH port forwarding; Local, and Remote
I play VNs on my Mac too. With CrossOver (or if you like not to pay Wine) you can Play many VNs. Visual novels steam. I don't know how hard it is to run an android or DS emulator on a mac, but I'm sure they're out there.PS: I'm a big fan and user of VNDS, and would be happy to help if you need any!I have a Nintendo DS so this sounds like a great option! I'll look into this!
[edit]Local Port Forwarding
A real world example:
Suppose that you wish to manage your router's settings from anywhere over the Internet. You want to use a GUI interface, but you don't want to enable management via remote HTTP (insecure) or HTTPS (resource-intensive). How do you accomplish this?
This is where SSH port forwarding comes in. This feature makes it possible to connect securely to the router's HTTP web interface, even when the interface has been configured to only be accessible by computers on the router's LAN.
First, 'Remote SSH Management' must be enabled under Administration -> Management if you wish to connect to your router from the WAN.
A local port forward can be established from the CLI with the following syntax:
ssh -L :: user@ -p
To explain more precisely what this command does: your computer establishes an SSH connection to ; a tunnel is created between your computer's , the , and on . Data sent to is transferred over the secure SSH connection to the , where it is then decrypted and forwarded to on .
For instance, if your router's WAN IP address is 12.23.34.35, its remote administration SSH port is 9999 and its LAN-accessible web interface is at port 80:
ssh -L 12345:localhost:80 root@12.23.34.45 -p 9999
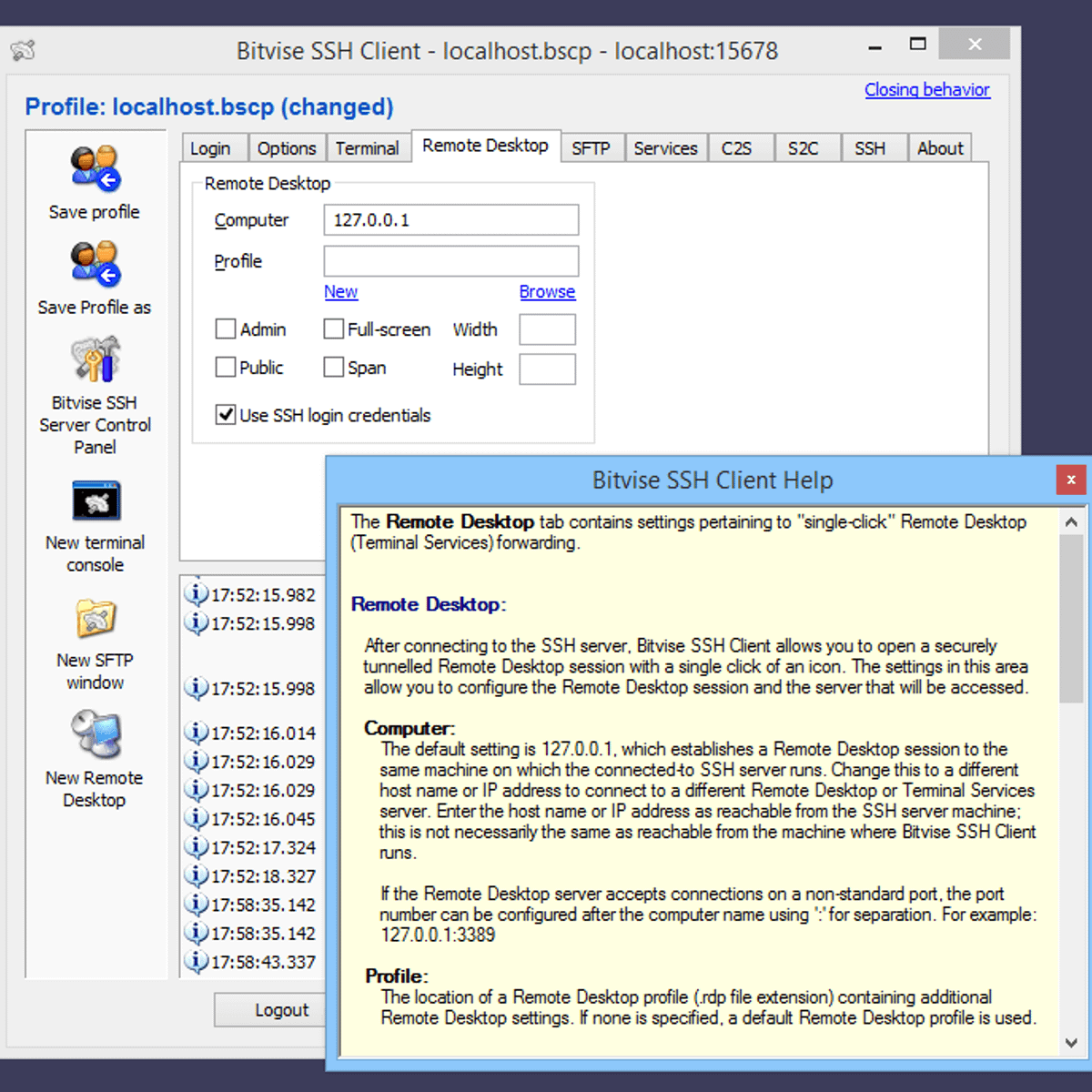
The resulting connection:
Open your local browser window and point it to http://localhost:12345, and you should be able to log into the router's web interface as if you were on the router's local area network. This connection is secure!
If you're using PuTTY for SSH, the procedure is similar; SSH port forwarding is configured under SSH -> Tunnels
(NOTE: the PuTTY connection fails after web interface login when using PuTTY from the Ubuntu repositories, giving error: 'SSH2_MSG_CHANNEL_FAILURE for nonexistent channel 257' --Brandonc 23:44, 2 August 2012 (CEST))
For more information related to the tunnel setup see here:Forum Discussion
[edit]Remote Port Forwarding
This is useful to tunnel things like RDP (Remote Desktop) through an encrypted SSH tunnel over the internet. For example, you want to be able to access your work computer from home.
If you had:
HomePC <-> Router <-> Internet <-> Firewall <-> WorkPC
WorkPC, which is running RDP on port 3389, issues ssh -R 5555:localhost:3389 root@router.home
HomePC can use his RDP client to connect to port 5555 on the router and this would create an SSH tunnel which will connect HomePC to port 3389 on the WorkPC.
[edit]Requirements- DD-WRT v24 RC7+
- SSHd and SSH TCP Forwarding must be enabled under Services -> Secure Shell
- Remote SSH Management should be enabled as well, under Administration -> Management
Setting up a remote port forward is relatively straightforward when using the PuTTY utility under Windows.See Connections -> SSH -> Tunnels. Make sure your configuration includes parameters as illustrated above. Namely,
- Local and Remote ports should accept connections from other hosts
- Source port (port # on the router, should be > 1024)
- Destination IPAddress:Port
- Type: Remote
[edit]SCP
Secure Copy (SCP) allows one to copy files to and from the router and a remote host--usually a desktop machine.
Some good Windows clients to use are FileZilla and WinSCP.
Configure the client to use the Private Key you saved earlier, or use 'root' and the webinterface password
Remember: only the /tmp and /jffs partitions are writable!
[edit]Drop Bear
DropBear is an SSH client/server installed by default on the WRT54G. DropBear allows one to connect from the WRT54G to a remote SSH server for scp, etc. I don't believe SSHD needs to be enabled through the Web Interface in order to use the client portion of DropBear.
If you have an SSH server on your desktop machine (such as OpenSSH) you pull files from your desktop machine using the scp command. This can be used to copy files from your desktop machine in a Startup Script
aka the DD-WRT Linux shell
This is an 'ash' shell. Ash is a version of sh, literally 'A SHell' (A command Interpreter)
[edit]Basic Syntax
The Linux Command Shell (Ash) is not the same as the Windows/DOS command prompt.
/ (and not ) is used to separate directories in a path, just like the interweb.
In order to execute a command, the path for that command must be provided. This may either be a full path or a relative path.
[edit]Relative Path Operators
There are two relative path operators.
[edit]Examples
1) If you are in the /jffs/usr/bin directory and wish to run the /jffs/usr/bin/noip command use:
or
2) If you are in the /jffs/usr/bin directory and wish to run the /jffs/usr/kismet command use:
or
or
3) Relative paths can also be used as arguments. If you installed the noip package, you'd notice that the command is installed as /jffs/usr/bin/noip but its configuration file is installed as /jffs/etc/no-ip.conf When running noip, it is thus required to give it the path to its configuration file with the -c command. This can be done like:
or
notice that the first ./ brings us to /jffs/usr/. The second ./ brings us to /jffs/, and then the rest of the path can be appended.
4) While the other examples all showed how to save typing, you can also really screw around with relative paths. To launch the noip command in example 1, you could also use
Here we browse all the way back to the root / directory, then climb back up to /jffs/usr/bin, drop back down to /jffs/usr and then climb back up to /jffs/usr/bin.
Current path references of /./ are thrown in sporadically just to mix things up. Notice how /./ always references the then current path, not the original path of the shell when the command was entered.
[edit]Pipes and Redirects
The output of commands can be piped through other commands or redirected to devices and files.
< and > are the redirect operators. < Takes input from a device or file and routes it as input to the command given. > Takes output from a command and redirects it as input for a device or file.Ex: If you don't want to see the output of a command, redirect it to the null device:
| is the pipe character, and pipes the output through another command (for formatting, etc)Ex: the most common use of the pipe is to limit the output of a command:
This is extremely useful for commands like nvram show which list some 800-1200 lines. nvram show | more will list the results 1 page at a time.
[edit]Background processes
It is possible to run programs in the background (returning you to the command prompt immediately) by terminating your command with the & character.ex:
Make sure you add a space between your command and the ampersand or you will result with a File not found error.
[edit] WEB-GUI (http[s]) Special note
The built-in WEB-GUI command line interface (Diagnostics.asp page) allows only about 200 characters max per line.
Special characters such as ' or | must be entered after a
Example, if you want to set a text nvram value:
Instead of
Enter
[edit]Basic Commands
[edit]More Advanced Commands
These commands warrant their own wikis:
- write (part of CLI flash instructions)
PuTTY (All), HyperTerminal (WinXP and older), minicom (Linux), picocom (Linux), terminalbpp (Win)
Telnet And Ssh Client For Mac

The DD-WRT firmware can use user/pass logon or only allows connections from clients whose public keys are manually entered via the web interface. Multiple keys can be entered by placing them on separate lines.
If you want to use user/password to login using SSH use user 'root' with the password you set in the webinterface
Actually you can manually set (via telnet or ssh) the sshd_authorized_keys nvram variable.ie nvram set sshd_authorized_keys=key1 key2 key3 etc
You can also manually edit /tmp/root/.ssh/authorized_keys and add keys (although these will disappear on a reboot unless you have a startup script altering them).
It is worth pointing out ssh keys are quite long strings of characters so if you paste them in youhave to be careful that you don't get any line breaks (ie it is one Long continuous line).or they will not work.
[edit]Setting Up
[edit]Public key method
Public key authentication is one of the most secure methods of logging into SSH. It functions similar to HTTPS, as all transmissions are encrypted with a key that only the client and server will have. Another plus..if you use this method instead of password authentication, no one will be able to crack away at your router trying to guess the password!
To enable it, first you should generate a Public/Private key pair on your desktop machine. This can be done through the 'Puttygen' utility if you're using either Putty or WinSCP as clients. Copy the public key to the clipboard and save the private key somewhere on your computer. There is no need to save the public key. If you forget it, you can instruct Puttygen to open your private key file rather than generating a new key pair and it will tell you your public key. Users of non-windows environments may use the ssh-keygen(1) utility:
Download iMovie 10.1.14 for Mac OS. IMovie is an integrated Apple-based application that serves users as an efficient, highly-effective and intuitive multimedia editing application. Create a new iMovie project. Learn how to set up a new project and add content to it on your. Just click to download and install on your Mac or iOS device. Download iMovie for iOS Download iMovie for macOS. Clips is a free iOS app for making and sharing fun videos with text, effects, graphics and more. Download imovie for mac. Download and Install iMovie. Download for PC - server 1 - MAC: Download for MacOS - server 1 - Free Thank you for visiting our site. Have a nice day! From the first scene to the last. Whether you're using a Mac or an iOS device.
It is recommended that you don't secure your key pair with a password, as this will make things easier for you, although somewhat less secure.
- Using the Web Interface, go to the Administration tab. (in v24 use Services tab)
- Under the Services sub-tab, Enable SSHd in the Secure Shell section. If new options don't appear, Save Settings
- Paste your public key in the authorized key of the SSHD section that has now expanded. You will need to generate this on your desktop if you don't have one yet.
- Save and Apply Settings
NOTE: The format of the public key when pasted has to be 'ssh-rsa', space, key, space, comment. Here is an example: (please note that there should be no line feed at the end)
Alternate method:
Remember to enter your key as an entire characters line (no space, tab..)
In Putty, you can enable key authentication by opening the SSH authentication configuration (Connection -> SSH -> Auth) and entering or browsing to your private key file. Also make sure your auto-login username is root (in Connection -> Data).
[edit]Password Login method
If you don't want the hassle of generating ssh keys, you may use the password logon method. However, please be aware that this method is much less secure! (passwords may be truncated to 8 characters or less)
- Using the Web Interface, go to the Administration tab. (in v24 use Services tab)
- Under the Services sub-tab, Enable SSHd in the Secure Shell section. If new options don't appear, Save Settings
- Enable Password Login to enable the password login
- Save and Apply Settings
After this you may login as user 'root' with the password you set for the webinterface
Install Telnet Mac
[edit]Automatic Login (for shell scripts)
The Dropbear SSH client allows you to specify the password through an environment variable. This is useful when you need dd-wrt to auto-login to another host via SSH.
[edit]Security Tips
- Choose a random, non-standard port number >1024, especially if you enabled SSH access from the Internet! Most attackers will use a port scanner that only scans for common open ports by default. Scanning all 65535 ports is much slower for them, which makes it more difficult to find an attack vector and also more likely to be flagged by an Intrusion Detection System.
- Memorize, or record somewhere safe, your router's key fingerprint! In the process of logging into your router, if you see that the key fingerprint matches, you can rest assure noone is spying on your connection (i.e. via man-in-the-middle attack). If the key fingerprint does NOT match (your SSH client would likely notify you of this), something is wrong and you should consider terminating the connection immediately! (Note: the router's key fingerprint may change upon reset and/or upgrade, as it will likely generate a new key pair)
- For even more added security when using the public key method, you can password protect your private key. This way, if someone malicious happens to get ahold of it, they will still not be able to log into your router without first cracking the password of the key. Otherwise, if the keys are unprotected, anyone who stumbles upon them could likely gain immediate root access to your router and network.
[edit]SSH Shell Client
Provides a secure alternative to standard telnet.
A good Windows Client to use is Putty
Configure the client to use the Private Key you saved earlier.
Most Linux distros have telnet and SSH clients by default.
[edit]SSH Port Forwarding
SSH port forwarding is the ability to create encrypted tunnels to pass traffic through, sort of like a VPN. Below we will discuss two different approaches to SSH port forwarding; Local, and Remote
I play VNs on my Mac too. With CrossOver (or if you like not to pay Wine) you can Play many VNs. Visual novels steam. I don't know how hard it is to run an android or DS emulator on a mac, but I'm sure they're out there.PS: I'm a big fan and user of VNDS, and would be happy to help if you need any!I have a Nintendo DS so this sounds like a great option! I'll look into this!
[edit]Local Port Forwarding
A real world example:
Suppose that you wish to manage your router's settings from anywhere over the Internet. You want to use a GUI interface, but you don't want to enable management via remote HTTP (insecure) or HTTPS (resource-intensive). How do you accomplish this?
This is where SSH port forwarding comes in. This feature makes it possible to connect securely to the router's HTTP web interface, even when the interface has been configured to only be accessible by computers on the router's LAN.
First, 'Remote SSH Management' must be enabled under Administration -> Management if you wish to connect to your router from the WAN.
A local port forward can be established from the CLI with the following syntax:
ssh -L :: user@ -p
To explain more precisely what this command does: your computer establishes an SSH connection to ; a tunnel is created between your computer's , the , and on . Data sent to is transferred over the secure SSH connection to the , where it is then decrypted and forwarded to on .
For instance, if your router's WAN IP address is 12.23.34.35, its remote administration SSH port is 9999 and its LAN-accessible web interface is at port 80:
ssh -L 12345:localhost:80 root@12.23.34.45 -p 9999
The resulting connection:
Open your local browser window and point it to http://localhost:12345, and you should be able to log into the router's web interface as if you were on the router's local area network. This connection is secure!
If you're using PuTTY for SSH, the procedure is similar; SSH port forwarding is configured under SSH -> Tunnels
(NOTE: the PuTTY connection fails after web interface login when using PuTTY from the Ubuntu repositories, giving error: 'SSH2_MSG_CHANNEL_FAILURE for nonexistent channel 257' --Brandonc 23:44, 2 August 2012 (CEST))
For more information related to the tunnel setup see here:Forum Discussion
[edit]Remote Port Forwarding
This is useful to tunnel things like RDP (Remote Desktop) through an encrypted SSH tunnel over the internet. For example, you want to be able to access your work computer from home.
If you had:
HomePC <-> Router <-> Internet <-> Firewall <-> WorkPC
WorkPC, which is running RDP on port 3389, issues ssh -R 5555:localhost:3389 root@router.home
HomePC can use his RDP client to connect to port 5555 on the router and this would create an SSH tunnel which will connect HomePC to port 3389 on the WorkPC.
[edit]Requirements- DD-WRT v24 RC7+
- SSHd and SSH TCP Forwarding must be enabled under Services -> Secure Shell
- Remote SSH Management should be enabled as well, under Administration -> Management
Setting up a remote port forward is relatively straightforward when using the PuTTY utility under Windows.See Connections -> SSH -> Tunnels. Make sure your configuration includes parameters as illustrated above. Namely,
- Local and Remote ports should accept connections from other hosts
- Source port (port # on the router, should be > 1024)
- Destination IPAddress:Port
- Type: Remote
[edit]SCP
Secure Copy (SCP) allows one to copy files to and from the router and a remote host--usually a desktop machine.
Some good Windows clients to use are FileZilla and WinSCP.
Configure the client to use the Private Key you saved earlier, or use 'root' and the webinterface password
Remember: only the /tmp and /jffs partitions are writable!
[edit]Drop Bear
DropBear is an SSH client/server installed by default on the WRT54G. DropBear allows one to connect from the WRT54G to a remote SSH server for scp, etc. I don't believe SSHD needs to be enabled through the Web Interface in order to use the client portion of DropBear.
If you have an SSH server on your desktop machine (such as OpenSSH) you pull files from your desktop machine using the scp command. This can be used to copy files from your desktop machine in a Startup Script
aka the DD-WRT Linux shell
This is an 'ash' shell. Ash is a version of sh, literally 'A SHell' (A command Interpreter)
[edit]Basic Syntax
The Linux Command Shell (Ash) is not the same as the Windows/DOS command prompt.
/ (and not ) is used to separate directories in a path, just like the interweb.
In order to execute a command, the path for that command must be provided. This may either be a full path or a relative path.
[edit]Relative Path Operators
There are two relative path operators.
[edit]Examples
1) If you are in the /jffs/usr/bin directory and wish to run the /jffs/usr/bin/noip command use:
or
2) If you are in the /jffs/usr/bin directory and wish to run the /jffs/usr/kismet command use:
or
or
3) Relative paths can also be used as arguments. If you installed the noip package, you'd notice that the command is installed as /jffs/usr/bin/noip but its configuration file is installed as /jffs/etc/no-ip.conf When running noip, it is thus required to give it the path to its configuration file with the -c command. This can be done like:
or
notice that the first ./ brings us to /jffs/usr/. The second ./ brings us to /jffs/, and then the rest of the path can be appended.
4) While the other examples all showed how to save typing, you can also really screw around with relative paths. To launch the noip command in example 1, you could also use
Here we browse all the way back to the root / directory, then climb back up to /jffs/usr/bin, drop back down to /jffs/usr and then climb back up to /jffs/usr/bin.
Current path references of /./ are thrown in sporadically just to mix things up. Notice how /./ always references the then current path, not the original path of the shell when the command was entered.
[edit]Pipes and Redirects
The output of commands can be piped through other commands or redirected to devices and files.
< and > are the redirect operators. < Takes input from a device or file and routes it as input to the command given. > Takes output from a command and redirects it as input for a device or file.Ex: If you don't want to see the output of a command, redirect it to the null device:
| is the pipe character, and pipes the output through another command (for formatting, etc)Ex: the most common use of the pipe is to limit the output of a command:
This is extremely useful for commands like nvram show which list some 800-1200 lines. nvram show | more will list the results 1 page at a time.
[edit]Background processes
It is possible to run programs in the background (returning you to the command prompt immediately) by terminating your command with the & character.ex:
Make sure you add a space between your command and the ampersand or you will result with a File not found error.
[edit] WEB-GUI (http[s]) Special note
The built-in WEB-GUI command line interface (Diagnostics.asp page) allows only about 200 characters max per line.
Special characters such as ' or | must be entered after a
Example, if you want to set a text nvram value:
Instead of
Enter
[edit]Basic Commands
[edit]More Advanced Commands
These commands warrant their own wikis:
- write (part of CLI flash instructions)
PuTTY (All), HyperTerminal (WinXP and older), minicom (Linux), picocom (Linux), terminalbpp (Win)
Telnet And Ssh Client For Mac
Script Examples
Sshfs
Startup Scripts
SSH access from internet
Tunnel all traffic over ssh using remote windows machine and Putty
Telnet Client For Mac
Wikipedia's SSH article
Linux Shell Scripting Tutorial
Telnet/SSH BusyBox Commands
